Groundbreaking study fills critical gap in evidence-based treatment options for DFUs with exposed structure.
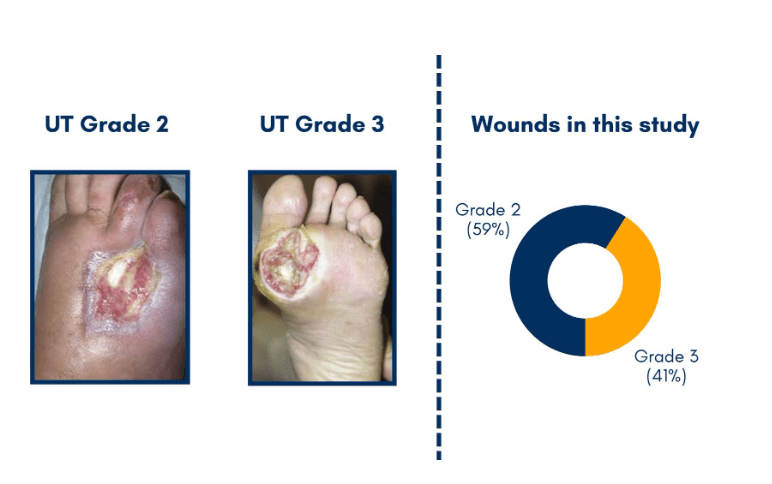
DFUs classified as University of Texas (UT) grades 2 and 3 are some of the most challenging wounds to treat, and are associated with higher rates of infection, delayed healing, and increased risk of amputation.1
The increased risk associated with grade 2 and 3 diabetic foot ulcers stems from their depth and complexity.
Increased Depth and Complexity creates:
For patients with University of Texas (UT) grade 2 and 3 ulcers – the severe cases where bone or tendon is exposed – the stakes of having an open wound are high:
These complex ulcers have long been a challenge for clinicians, with limited evidence-based treatment options available. Despite the devastating impact these deep ulcers often have on patients and their families, there has been a lack of large-scale, randomized controlled trials to investigate care options.
Wound Closed
at 16 Weeks
Significant Results
(95% CI: 1.48 – 4.56)
The new study, titled Intact Fish Skin Graft to Treat Deep Diabetic Foot Ulcers: The Odinn Trial, changes that. It found that at 16 weeks, 44.0% of wounds treated with fish skin grafts (IFSG) had healed, compared to only 26.4% with standard of care (SOC) (p<0.001).
The trial involved 255 patients at 15 care centers across four countries.
![]()
The Odinn trial represents true level 1 evidence that advanced therapeutics such as intact fish skin grafts make a difference in the real world of deep and complex diabetic foot wounds
Dr. John Lantis, MD, Site-Chief of Surgery at the Mount Sinai West Hospital, and study co-author.

The Odinn study is a landmark study representing the first large-scale RCT focused exclusively on UT grade 2 and 3 DFUs, involving 255 patients across 15 centers. The scale and focus of this trial provide unprecedented insights into the management of these complex wounds, offering clinicians and patients a new level of evidence in an area where it has been lacking. By specifically targeting these severe ulcers, the study addresses a critical unmet need in diabetic foot care.
The primary funding sources were the European Commission Fast Track to Innovation Horizon 2020 (80%) and Kerecis Ltd. (13%).
The study focused on complex ulcers with a higher associated healthcare cost. The Odinn study was designed to show efficacy for Intact fish skin grafts in complex DFUs with exposed bone and tendon (UT 2 and 3). The study was designed to fulfill all the clinical trial criteria of the AHRQ evidence criteria for Skin substitutes in the USA and criteria of European insurance programs to offer reimbursement coverage.
Moulik, P. K., Mtonga, R., & Gill, G. V. (2003). Amputation and mortality in new-onset diabetic foot ulcers stratified by etiology. Diabetes Care, 26(2), 491-494.
